
Hail up to 13 cm in Brisbane
- Dec 30 2025
- /
- 179

A cable is a thick wire or a group of wires inside a rubber or plastic covering and used to carry electricity or electronic signals. Today, the term 'cable' is often used to refer to television systems in which the signals are sent along underground wires rather than by radio waves.
Electrical cables connect two or more devices, enabling the transfer of electrical signals or power from one device to the other. Cables are used extensively in electronic devices for power and signal circuits.
Data cables are any media that allows baseband transmissions (binary 1, 0s) from a transmitter to a receiver. Data cables are used to transmit information between systems such as servers, personal computers and other hardware.

We tend to think of digital communication as a new idea but in 1844 Samuel Morse sent a message 37 miles from Washington D.C. to Baltimore, using his new invention, 'The Telegraph'.
The types of data cables used in modern networks include:

A structured cabling system is a complete system of cabling and associated hardware that provides a comprehensive telecommunications infrastructure. This infrastructure serves a wide range of uses, such as providing telephone services or transmitting data through computer networks.
Data cables are usually made of rubber, Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) or Teflon. The shield (metal envelope) surrounding the cables protects the data transmitted on the medium from interference (also called noise) that could corrupt the data.
Fibre optic cable uses light to transmit data. Over the last 20 years, fibre optic lines have dominated and transformed the long distance telephone industry. When fibre replaces copper for long distance calls and internet traffic, it dramatically lowers costs.
Fibre optic transmissions are faster than copper wire transmissions. Fibre optic versus copper wire transmission can be boiled down to the speed of photons versus the speed of electrons. Photons travel at the speed of light whereas electrons, as occurring in nature and as used in copper wire, travel at less than one percent of the speed of light.
Popular applications for the use of data cabling include:

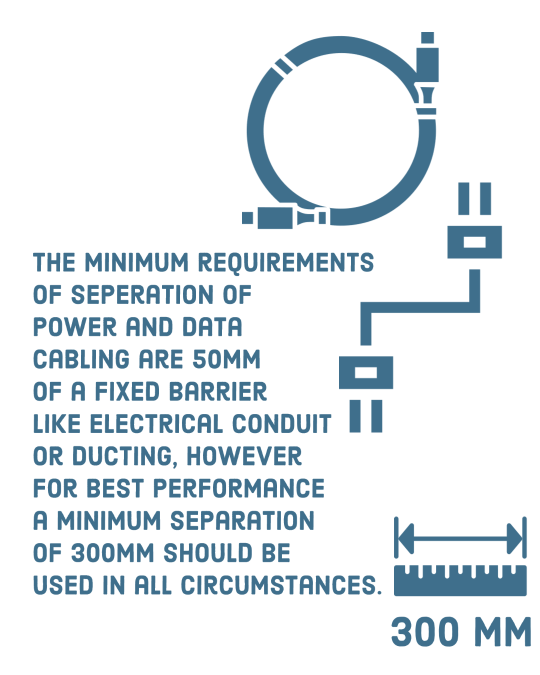
Current standards clearly define the separation between electrical power and data cables. Telecommunications cabling must be separated from electrical cabling.
The minimum requirements of separation of power and data cabling are 50mm of a fixed barrier like electrical conduit or ducting, however for best performance a minimum separation of 300mm should be used in all circumstances.
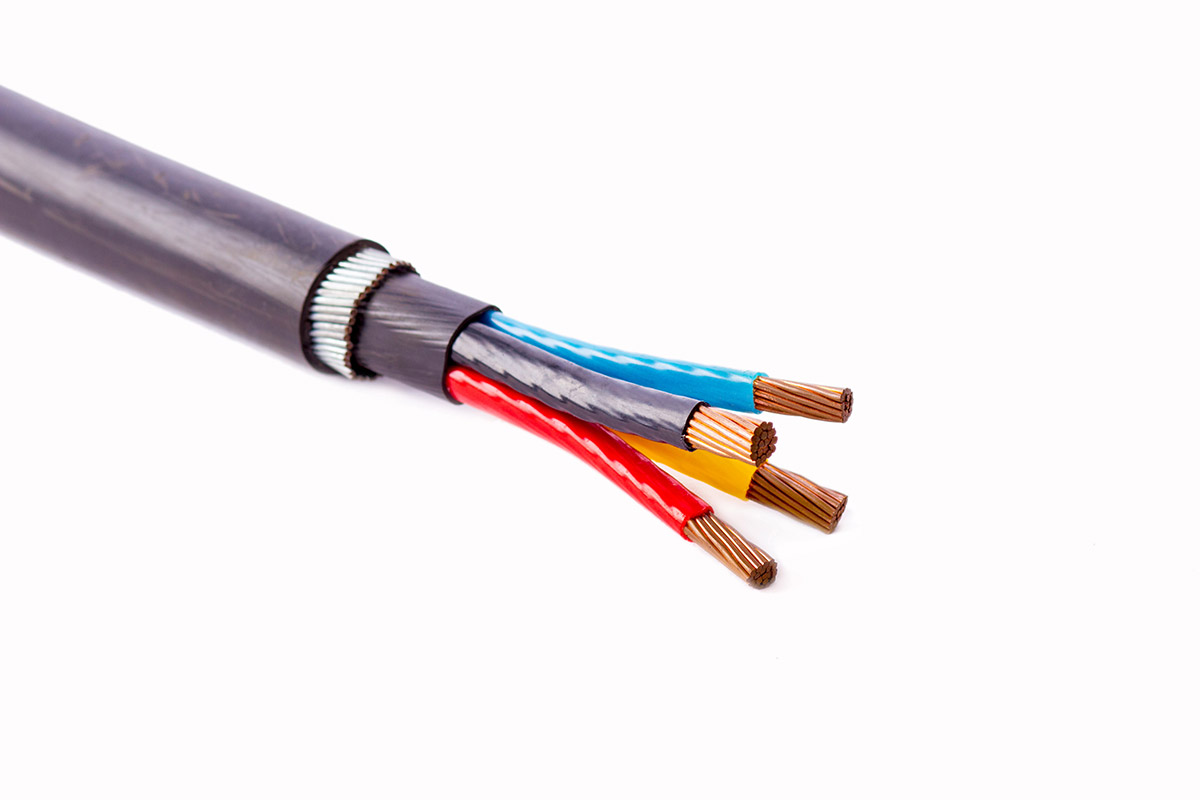
An armoured cable is a type of electrical cable that has an extra protective layer to shield it from damage, making it more durable and resistant to external forces. This layer, known as the armour, is typically made of steel or aluminum and helps protect the cable from mechanical stress, rodents, and environmental hazards like moisture or chemicals. They are often used in underground scenarios.
Engaging licensed telecommunications technicians to install data cabling systems has several advantages. For instance, qualified electricians will use high-quality data cables and will consult you about the costs. Quality cables make a huge difference in optimising your business computers and devices.
Insurance policies and product warranties often specify your policy will be void if you use an unregistered cabler.
All registered cablers are required to undertake appropriate training modules or training competencies to ensure that they are competent to perform the cabling work according to the 'Wiring Rules', which ensure safety to consumers, cablers and the network.
If a cabler is registered, they will show you their registration card. You can check that their registration is current by contacting their registrar.
https://www.acma.gov.au/work-registered-cabler
Under the registration system, there are three types of registrations - Open, Restricted and Lift.
Below is a summary of the type of work that can be done under each registration. For full details, refer to the Telecommunications Cabling Provider Rules 2014 (CPR)
CPRs cover all sectors that involve customer cabling work, including telephone, data, fire and security alarm systems cabling, that connect or are intended to connect with the telecommunications network. This work must be performed by a registered cabler or under the direct supervision of a registered cabler. There are no longer any exemptions to work on security, fire or computing cabling without registration.
Weiss Electrical - Brisbane have been providing high quality cabling and data services for over 25 years. From small residential jobs and new home installs and renovations to large commercial data centre fit-outs. Weiss provide licensed and highly skilled staff who can assist in the following areas of data cabling:










Check out our amazing 9 STAR QUALITY GUARANTEE